Tag: Fort Sumter SC
Wikipedia says: Fort Sumter is a sea fort built on an artificial island protecting Charleston, South Carolina, from naval invasion. Its origin dates to the War of 1812 when the British invaded Washington by sea. It was still incomplete in 1861 when the Battle of Fort Sumter began the American Civil War. It was severely damaged during the war, left in ruins, and although there was some rebuilding, the fort as conceived was never completed.
The building of Fort Sumter
Named after General Thomas Sumter, a Revolutionary War hero, Fort Sumter was built after the 1814 Burning of Washington during the War of 1812 as one of the third system of U.S. fortifications, to protect American harbors from foreign invaders such as Britain. Built on an artificial island in the middle of the channel that provides Charleston with natural shelter, Fort Sumter would dominate the harbor, reinforcing the protection provided by the shore batteries at Fort Moultrie, Fort Wagner, and Fort Gregg.
The island was originally a sand bar. In 1827, engineers performed measurements of the depths (depth sounding) and concluded that it was a suitable location for a fort. Construction began in 1829 Seventy thousand tons of granite were transported from New England to build up the artificial island. By 1834, a timber foundation that was several feet beneath the water had been laid. However, the decision was made to build a (stronger) brick fort. If completed, it would have been one of the strongest forts in the world.
The brick fort is five-sided, 170 to 190 feet (52 to 58 m) long, with walls five feet (1.5 m) thick, standing 50 feet (15.2 m) over the low tide mark. Although never completed, it was designed to house 650 men and 135 guns in three tiers of gun emplacements.
Construction dragged out because of title problems, then problems with funding such a large and technically challenging project. Unpleasant weather and disease made it worse. The exterior was finished but the interior and armaments were never completed.
Ownership
Early in the nineteenth century, South Carolina had owned multiple forts, namely Fort Moultrie, Castle Pinckney, and Fort Johnson, but ceded them, along with sites for the future erection of forts, to the United States in 1805. The forts were of questionable military value and costly to maintain, so when asked to cede them, the state complied. This was not the last time that South Carolina would cede forts to the United States; on December 17, 1836, South Carolina officially ceded all “right, title and, claim” to the site of Fort Sumter to the United States.
Civil War
Fort Sumter is notable for two battles, the first of which began the American Civil War. It was one of a number of special forts planned after the War of 1812, combining high walls and heavy masonry, and classified as Third System, as a grade of structural integrity. Work started in 1829, but was incomplete by 1861, when the Civil War began.
The attack on Fort Sumter is generally taken as the beginning of the American Civil War—the first shots fired. Certainly it was so taken at the time—citizens of Charleston were celebrating. The First Battle of Fort Sumter began on April 12, 1861, when South Carolina Militia artillery fired from shore on the Union garrison. These were, both sides agreed, the first shots of the war. The bombardment continued all day, watched by many happy civilians. The fort had been cut off from its supply line and surrendered the next day. Major Robert Anderson took the flag with him as they evacuated.
The Second Battle of Fort Sumter (September 8, 1863) was a failed attempt by the Union to retake the fort, dogged by a rivalry between army and navy commanders. Although the fort was reduced to rubble, it remained in Confederate hands until it was evacuated as General Sherman marched through South Carolina in February 1865.
A widely announced “End of the War” celebration took place at Fort Sumter on April 14, 1865. The now-Major General Anderson, though ill and retired, came to the ceremony and raised the flag. The incident is forgotten today because President Lincoln was shot that evening.
Preparing for war
On December 26, 1860, only six days after South Carolina seceded from the Union, U.S. Army Major Robert Anderson abandoned the indefensible Fort Moultrie, spiking its large guns, burning its gun carriages, and taking its smaller cannon with him. He secretly relocated companies E and H (127 men, 13 of them musicians) of the 1st U.S. Artillery to Fort Sumter on his own initiative, without orders from his superiors. He thought that providing a stronger defense would delay an attack by South Carolina militia. The fort was not yet complete at the time and fewer than half of the cannons that should have been available were in place, due to military downsizing by President James Buchanan.
In a letter delivered January 31, 1861, South Carolina Governor Pickens demanded of President Buchanan that he surrender Fort Sumter because “I regard that possession is not consistent with the dignity or safety of the State of South Carolina.” Over the next few months repeated calls for evacuation of Fort Sumter from the government of South Carolina and then from Confederate Brigadier General P. G. T. Beauregard were ignored. Union attempts to resupply and reinforce the garrison were repulsed on January 9, 1861 when the first shots of the war, fired by cadets from the Citadel, prevented the steamer Star of the West, hired to transport troops and supplies to Fort Sumter, from completing the task.
After realizing that Anderson’s command would run out of food by April 15, 1861, President Lincoln ordered a fleet of ships, under the command of Gustavus V. Fox, to attempt entry into Charleston Harbor and supply Fort Sumter. The ships assigned were the steam sloops-of-war USS Pawnee and USS Powhatan, transporting motorized launches and about 300 sailors (secretly removed from the Charleston fleet to join in the forced reinforcement of Fort Pickens, Pensacola, FL), armed screw steamer USS Pocahontas, Revenue Cutter USRC Harriet Lane, steamer Baltic transporting about 200 troops, composed of companies C and D of the 2nd U.S. Artillery, and three hired tugboats with added protection against small arms fire to be used to tow troop and supply barges directly to Fort Sumter. By April 6, 1861, the first ships began to set sail for their rendezvous off the Charleston Bar. The first to arrive was Harriet Lane, the evening of April 11, 1861.
First Battle of Fort Sumter
On Thursday, April 11, 1861, Beauregard sent three aides, Colonel James Chesnut, Jr., Captain Stephen D. Lee, and Lieutenant A. R. Chisolm to demand the surrender of the fort. Anderson declined, and the aides returned to report to Beauregard. After Beauregard had consulted the Confederate Secretary of War, Leroy Walker, he sent the aides back to the fort and authorized Chesnut to decide whether the fort should be taken by force. The aides waited for hours while Anderson considered his alternatives and played for time. At about 3:00 a.m., when Anderson finally announced his conditions, Colonel Chesnut, after conferring with the other aides, decided that they were “manifestly futile and not within the scope of the instructions verbally given to us.” The aides then left the fort and proceeded to the nearby Fort Johnson. There, Chesnut ordered the fort to open fire on Fort Sumter.
On Friday, April 12, 1861, at 4:30 a.m., Confederate batteries opened fire on the fort, firing for 34 straight hours. Edmund Ruffin, noted Virginian agronomist and secessionist, claimed that he fired the first shot on Fort Sumter. His story has been widely believed, but Lieutenant Henry S. Farley, commanding a battery of two 10-inch siege mortars on James Island actually fired the first shot at 4:30 a.m.. No attempt was made to return the fire for more than two hours. The fort’s supply of ammunition was not suited for the task; also, there were no fuses for their explosive shells, which means that they could not explode. Only solid iron balls could be used against the Confederate batteries. At about 7:00 a.m., Captain Abner Doubleday, the fort’s second in command, was given the honor of firing the Union’s first shot, in defense of the fort. He missed, in part because Major Anderson did not use the guns mounted on the highest tier – the barbette tier, where the guns could engage the Confederate batteries better, but where the gunners would be more exposed to Confederate fire. The firing continued all day. The Union fired slowly to conserve ammunition. At night, the fire from the fort stopped, but the Confederates still lobbed an occasional shell into Sumter. On Saturday, April 13, the fort was surrendered and evacuated. During the attack, the Union colors fell. Lt. Norman J. Hall risked life and limb to put them back up, burning off his eyebrows permanently. A Confederate soldier bled to death having been wounded by a misfiring cannon. One Union soldier died and another was mortally wounded during the 47th shot of a 100-shot salute, allowed by the Confederacy. Afterward, the salute was shortened to 50 shots. Accounts, such as in the famous diary of Mary Chesnut, describe Charleston residents along what is now known as The Battery, sitting on balconies and drinking salutes to the start of the hostilities.
Union siege of Fort Sumter
Union efforts to retake Charleston Harbor began on April 7, 1863, when Rear Admiral Samuel Francis Du Pont, commander of the South Atlantic Blockading Squadron, led the ironclad frigate New Ironsides, the tower ironclad Keokuk, and the monitors Weehawken, Passaic, Montauk, Patapsco, Nantucket, Catskill, and Nahant in an attack on the harbor’s defenses. (The 1863 Battle of Fort Sumter was the largest deployment of monitors in action up to that time.) The attack was unsuccessful: the Union’s best ship, USS New Ironsides never effectively engaged, and the ironclads fired only 154 rounds, while receiving 2,209 from the Confederate defenders. Due to damage received in the attack, the USS Keokuk sank the next day, 1,400 yards (1,300 m) off the southern tip of Morris Island. Over the next month, working at night to avoid the attention of the Federal squadron, the Confederates salvaged Keokuk’s two eleven-inch Dahlgren guns. One of the Dahlgren guns was promptly placed in Fort Sumter.
The Confederates, in the meantime, were strengthening Fort Sumter. A workforce of just under 500 enslaved Africans, under the supervision of Confederate army engineers, were filling casemates with sand, protecting the gorge wall with sandbags, and building new traverse, blindages, and bombproofs. Some of Fort Sumter’s artillery had been removed, but 40 pieces still were mounted. Fort Sumter’s heaviest guns were mounted on the barbette, the fort’s highest level, where they had wide angles of fire and could fire down on approaching ships. The barbette was also more exposed to enemy gunfire than the casemates in the two lower levels of the fort.
A special military decoration, known as the Gillmore Medal, was later issued to all Union service members who had performed duty at Fort Sumter under the command of Major-General Quincy Adams Gillmore.
Fort Sumter Armaments, August 17, 1863
Left flank barbette: Two 10-inch (250 mm) columbiads
Left face barbette: Two 10-inch (250 mm) columbiads, two 8-inch (200 mm) columbiads, four 42-pounders
Left face, first tier casemates: Two 8-inch (200 mm) shell guns
Right face barbette: Two 10-inch (250 mm) columbiads, five rifled and banded 42-pounders
Right face, first tier casemates: Two 32-pounders
Right flank barbette: One XI-inch Dahlgren (From USS Keokuk), four 10-inch (250 mm) columbiads, one 8-inch (200 mm) Columbiad, one rifled 42-pounder, one 8-inch (200 mm) Brooke
Gorge barbette: Five rifled and banded 42-pounders, one 24-pounder
Salient, second tier casemates: Three rifled and banded 42-pounders
Parade: Two 10-inch (250 mm) seacoast mortars
Showing 1–16 of 131 resultsSorted by latest
-

Image ID: AZLU
$1.99 -

Image ID: AYPX
-

Image ID: AYPY
-

Image ID: AXBO
$4.99 -

Image ID: ARXX
$5.99 -

Image ID: ARXZ
$5.99 -

Image ID: ARZT
$3.99 -

Image ID: ARXD
$3.99 -

Image ID: APPX
$4.99 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Image ID: AOXO
$5.99 -
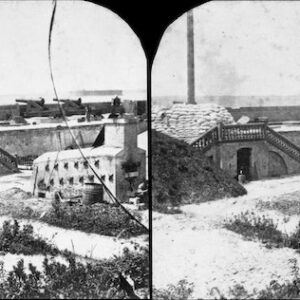
Image ID: ASES
$5.99 -
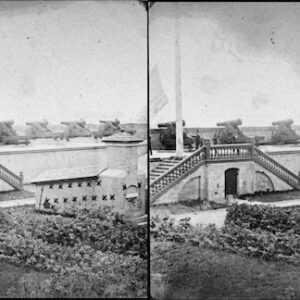
Image ID: ASFX
$5.99 -

Image ID: ASHB
$5.99 -

Image ID: ASEX
$5.99 -

Image ID: ASEY
$5.99 -
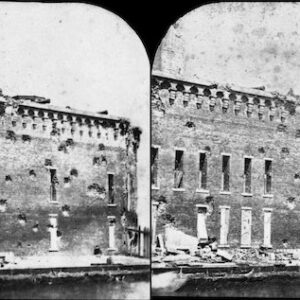
Image ID: ASFQ
$5.99